What is Phosphoric Acid and How is it Produced?
When you enjoy an ice-cold cola, the distinctive tang that hits your taste buds comes from phosphoric acid. So phosphoric acid is not harmful at low concentrations. But this acid does far more than just flavor your beverage: It’s a cornerstone of modern agriculture, with roughly 75% used to produce highly efficient phosphate fertilizers that nourish farmlands worldwide. The main application of phosphoric acid is in manufacturing fertilizers. About 90% of phosphoric acid produced each year is used by the fertilizer manufacturing industry. It’s essential for achieving smooth, corrosion-resistant metal surfaces. And in food processing, it acts as a safeguard, providing precise acidity and stability. So how is this ubiquitous “industrial lifeblood” produced?
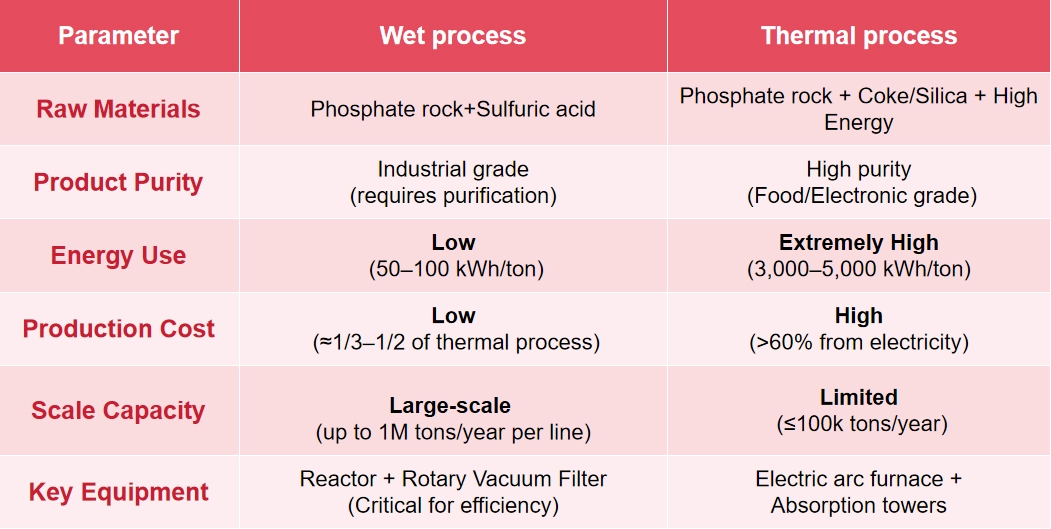
The production of phosphoric acid primarily relies on two fundamentally distinct processes: the thermal process and the wet process. The wet process dominates the industry, accounting for over 85% of global production due to its overwhelming economic advantages and large-scale capabilities.
The Mainstream “Magic” in Phosphorus Production: Wet Process
The thermal process is essentially a process of “high-temperature phosphorus refining”: phosphate ore, coke and silica are put into an electric arc furnace at a temperature of up to 1400-1500℃, and the phosphorus element in the ore is reduced to gaseous phosphorus, which is condensed and collected, then burned and oxidized into phosphorus pentoxide (P2O₅), and finally combined with water to form phosphoric acid. The core value of this method is to produce high-purity phosphoric acid, but the cost is amazing – each ton of phosphoric acid consumes 3000-5000 kWh of electricity, which is equivalent to the electricity consumption of 200 households a day.
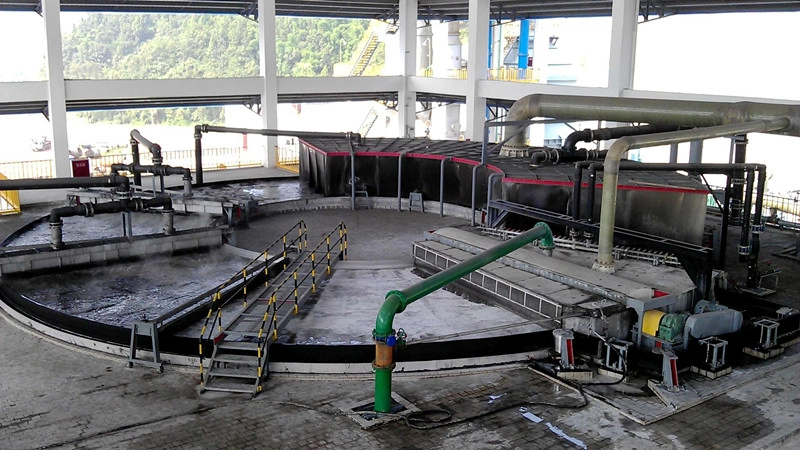
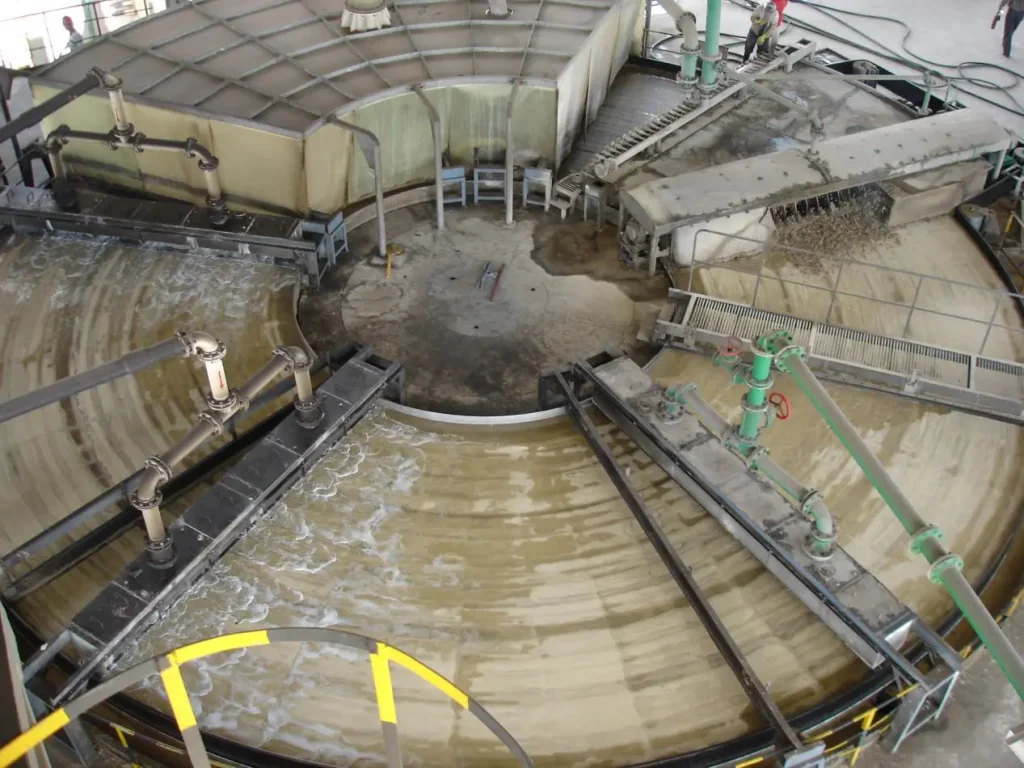
The wet process involves crushing phosphate rock and mixing it with sulfuric acid in a reaction vessel. An acid decomposition reaction releases phosphoric acid solution while generating solid calcium sulfate dihydrate (phosphogypsum) as a by-product. This process’s core competitiveness lies in low cost and large scale. The key technological breakthrough is solid-liquid separation. The mixed slurry formed after the reaction is as thick as mud, and traditional filtration equipment has low efficiency. However, modern rotary vacuum filters overcome this challenge: the continuous operation of different functional zones reduces filter cake moisture content below 18% and achieves phosphorus recovery exceeding 99%.
This continuous, automated separation delivers significant efficiency and cost advantages, establishing the wet process as the underlying industrial backbone – from agricultural fertilizers to cola’s sourness.
The following chart can help you visually understand the differences between these two production processes.
Therefore, we can intuitively understand the main reasons why the wet process phosphoric acid production process has become the mainstream, which can be expressed as the following three points:
Economy: Compared with the dry process, the energy cost of the wet process is reduced by more than 10 times, and the wet process can directly use low-grade phosphate rock as raw material, which can greatly reduce the cost. The reduction in price means that a million-ton plant can easily meet the bulk demand for fertilizers.
Technical compatibility: 75% of the world’s phosphoric acid is used for phosphate fertilizer production, and the phosphoric acid produced by the wet process has a perfect match for industrial grade purity. At the same time, the wet process can increase the purity of phosphoric acid to food grade through concentration, purification, thus covering the food market. In fact, China’s wet-process phosphoric acid extraction technology achieved a major breakthrough decades ago and has since been widely applied worldwide. In the 1990s, China relied heavily on imports of high-concentration phosphate fertilizers. NHD seized the opportunity and developed China’s first rotary table vacuum filter and rapid phosphoric acid extraction technology. This technology, utilizing a balanced extraction process involving multi-point acid addition and heat removal, combined with NHD’s extraction, mixing, and filtration equipment, significantly increased domestic phosphoric acid production.
The innovations of the rotary table vacuum filter: Rotary vacuum filtration greatly improves the solid-liquid separation efficiency, ensuring that the phosphoric acid recovery rate exceeds 99%. Compared with traditional filter presses, it can reduce 30% of energy consumption and half of the labor maintenance cost. Therefore, it is very important to choose the right solid liquid filtration equipment. In the early 2000s, only France could supply the 160m2 rotary table vacuum filter, the core equipment for an annual production of 300,000 tons of phosphoric acid. At that time, each unit cost over US$10 million and had long lead times. To address this pain point, NHD, in collaboration with a team of experts, independently innovated and successfully developed China’s first 160m2 rotary table vacuum filter. The widespread adoption of this equipment has helped propel China from a phosphate fertilizer importer to an exporter. And the company’s related technologies, including its “Large-Diameter Annular Table Processing Method,” have been awarded the China Patent Excellence Award. Currently, NHD has obtained 15 related patents, and the largest model of this equipment in use has been expanded to 320m2 (Guizhou Kailin Group’s 600,000 tons/year phosphoric acid project), and the design can be expanded to 380m2.
The essence of the wet process is to meet the largest demand with the lowest cost. As the “heart” of the wet process production line, the rotary table vacuum filter continues to consolidate this advantage through efficiency evolution: faster separation speed, lower phosphorus loss, smarter control, and ultimately turns phosphoric acid from a laboratory treasure into the “bulk blood” that supports modern agriculture and industry.
Selection Guide for Vacuum Filter: Four Steps to Lock in the Best Solution
Step 1: Key Challenges of Solid-Liquid Separation
- The Strong Corrosiveness of Phosphoric Acid: The required material is corrosion resistant.
- High Viscosity Filter Slurry: Easy to clog filter cloth.
- Solid-Liquid Separation Efficiency: The moisture content of the filter cake needs to be reduced.
- Continuous Production: Need to run 24 hours a day.
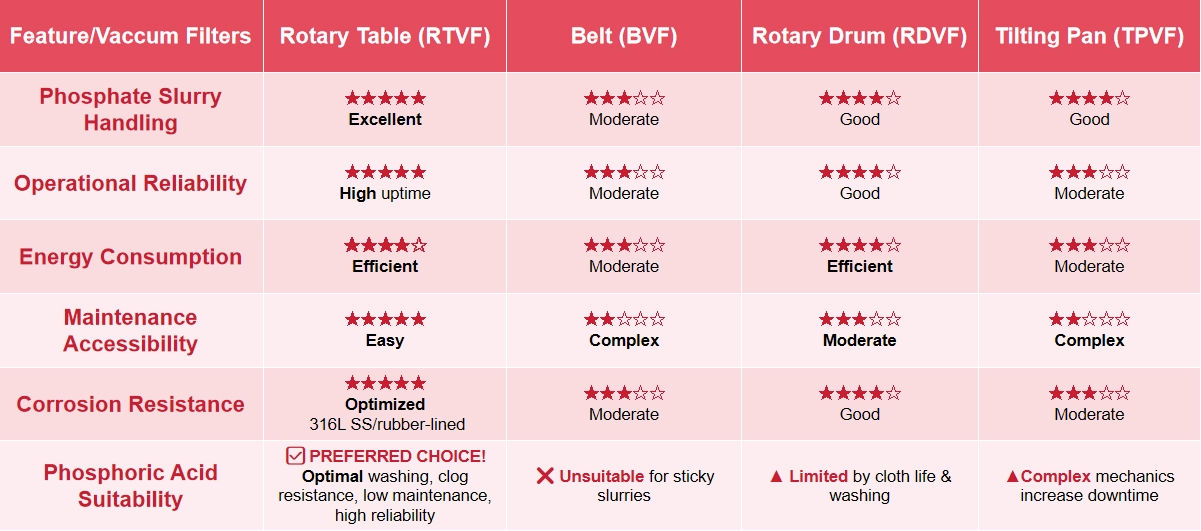
Step 2: Comparison Table of Vacuum Filters for Phosphoric Acid
Step 3: FOUR Key Parameters for Selecting Rotary Filter Machines
- Vacuum Intensity: ≥- 60kPa→The key to absorbing moisture from filter cake
- Corrosion Resistance: Stainless steel(316L)+ rubber lining
- Modular Design: Flat and leak-proof filter plates; Zoned vacuum system
- Energy Efficient: Reasonable distribution of wash water; High-torque output with low-power drive
Step 4: Why do Top Phosphate Companies Choose the Rotary Type?
- Cost:
- Significantly reduce the cost of the filter cloth.
- The intelligent system reduces manpower.
- Environmental Protection: Filter cake residual P2O5<8%
- Production Capacity:
- Operate continuously for 24 hours.
- A single production line can have an annual output capacity of 100,000+ tons.
The NHD’s Advantages in Rotary Vacuum Filtration
- Structural Optimization
Scientific filtration cell division and tapered support roller arrangement ensure even load distribution and stable operation. Strict flatness control is maintained across the entire pan. - Raw Material Adaptability
Multiple upgrades enable efficient processing of low-grade phosphate ores. This significantly expands the tablevacuum filter’s application scope. - High-Efficiency Nozzles
The new flatnozzle design features low power consumption and high scrubbing force. Combined with anti-block nozzle strainers, it saves more water. - Anti-Scaling Distributor Valve
The lower-center valve with steep inclination prevents gypsum scaling and blockages. This reduces cleaning frequency and boosts operational rate. - Adjustable Distribution System
The plate-type overflow systemensures uniform slurry distribution and optimizes cake washing and drying performance. - Rapid Maintenance Design
Arc-shaped press strips prevent scaling in retention slots, dramatically reducing cloth replacement time.
NHD has cooperated with the US WesTech Engineering Company on a rotary table vacuum filter modification project. To meet the customer’s needs, NHD sent a team of process, technology and equipment engineers to conduct on-site inspections and innovatively proposed a high-level installation solution. After the equipment was put into production, the 72-hour continuous operation test showed that the daily processing capacity reached 562 tons (the customer required 558 tons/24 hours), the gypsum water-soluble phosphorus content was 0.47 (better than the customer’s 0.5 index requirement), and all performance parameters exceeded the standards.
Conclusion
The Rotary Vacuum Filter is not only an equipment upgrade, but also a reconstruction of the production process. Its compact design, intelligent response and extreme corrosion resistance are driving wet-process phosphoric acid production towards a new era of zero downtime, near-zero loss and ultra-low emissions.
NHD is the industry benchmark for global industrial liquid filtration systems, especially in the field of rotary vacuum filtration technology. Since its establishment, the company has been continuously innovating for more than 30 years. With over 300 rotary table vacuum filters already in operation across the phosphate chemical industry, NHD is committed to delivering the most advanced production technologies combined with the most durable and reliable products. Our mission goes beyond supporting China’s phosphate industry—we aim to safeguard global food security. We look forward to more cooperation in the future. Feel free to reach out to [email protected] for more details.